How surgical instruments are sterilized ?
Surgical instruments sterilization stands as the cornerstone of modern healthcare, a vital shield against infections and a guardian of patient safety. From meticulous cleaning to combating microbial threats, its significance cannot be overstated. Healthcare professionals must master its methods, as inadequate sterilization poses grave risks, from surgical site infections to broader healthcare-associated perils. Every sanitized instrument safeguards lives, protects workers, and mitigates costs. This article explores the intricacies of surgical instrument sterilization, providing invaluable insights for healthcare facilities to uphold the gold standard of patient safety and care.
I. Understanding Sterilization:
- Cutting and Dissecting Instruments: Including scalpels, scissors, and surgical blades used for incisions and tissue dissection.
- Grasping and Holding Instruments: Such as forceps and clamps, utilized for holding tissues, organs, or sutures during surgery.
- Hemostatic Instruments: Including hemostats and ligature instruments, essential for controlling bleeding during surgical procedures.
- Retractors: Instruments like surgical hooks and retractors are used to hold back tissues and organs, providing better exposure of the surgical area.
Suturing and Stapling Instruments: These tools, including needles, needle holders, and staplers, are employed for wound closure and tissue approximation.
Effective Sterilization of Surgical
- Prevents Pathogen Transmission: Proper sterilization reduces the risk of surgical site infections (SSI) and other healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) by eliminating pathogens from surgical instruments.
- Ensures Patient Safety: Meticulous sterilization of each instrument type is crucial for protecting patient health and minimizing the risk of complications during surgical procedures.
- Adheres to Sterilization Standards: Compliance with sterilization standards and regulations, including those set forth by regulatory bodies like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO), is essential for maintaining patient safety and quality care.
- Mitigates Antibiotic Resistance: Stringent sterilization practices help mitigate the spread of antibiotic-resistant pathogens, safeguarding patient health and reducing the risk of infections.

II. Pre-Sterilization Preparation :
Preparation before sterilization is a critical step in ensuring the effectiveness of the sterilization process and maintaining patient safety during surgical procedures. This phase involves several key activities, including cleaning and decontamination of surgical instruments, inspection for damage or defects, and sorting instruments for appropriate sterilization methods.
i. Cleaning and Decontamination :
Healthcare professionals thoroughly clean and decontaminate surgical instruments to remove organic material, blood, and contaminants. They utilize enzymatic detergents, ultrasonic cleaners, or mechanical scrubbing to ensure debris removal. Research from the Journal of Infection Prevention stresses proper cleaning’s importance, as inadequate cleaning can compromise sterilization efficacy and increase HAIs risk.
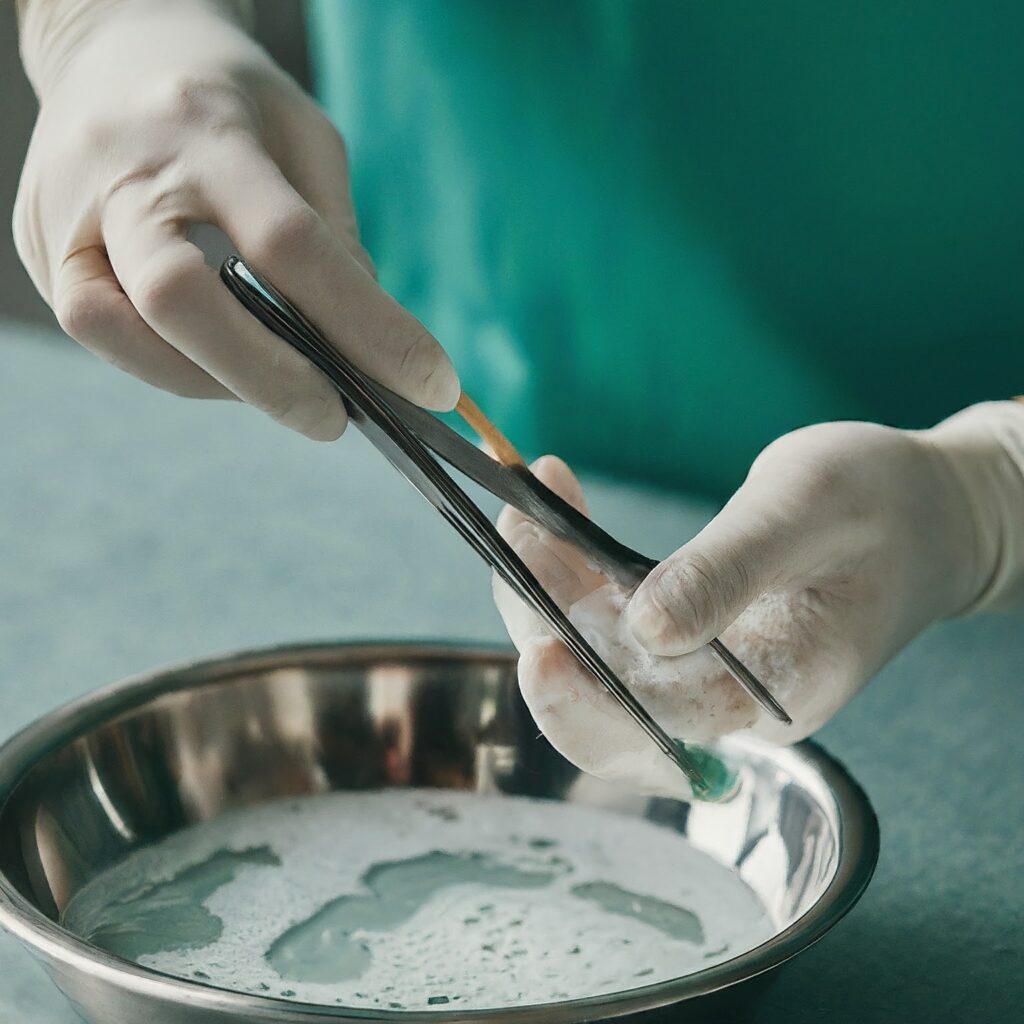
ii. Sorting for Appropriate Sterilization Methods:
Upon cleaning and inspection, healthcare professionals categorize surgical instruments by material, size, and complexity. Instruments undergo specific sterilization methods like autoclaving, EtO sterilization, or gas plasma sterilization, depending on characteristics. This sorting ensures efficient sterilization, minimizing contamination risks and enhancing patient safety
III. Sterilization Methods :
i. Autoclaving :
- Autoclaving is a widely used method for sterilizing surgical instruments and medical equipment. It involves exposing instruments to high-pressure steam at temperatures typically ranging from 121°C to 134°C.
- The autoclave process works by creating steam under pressure, which penetrates and destroys microbial life on instruments, effectively sterilizing them. The exposure time varies depending on the size and complexity of the load.
- Temperature and pressure requirements are crucial factors in ensuring the effectiveness of autoclaving. Proper validation and monitoring of these parameters are essential to guarantee sterilization efficacy
.

ii. Ethylene Oxide (EtO) Sterilization :
Ethylene oxide (EtO) sterilization treats heat-sensitive instruments by exposing them to ethylene oxide gas in a sealed chamber.
Paramount safety measures include proper ventilation and personal protective equipment (PPE) to mitigate risks to healthcare workers and patients, given ethylene oxide’s flammable and carcinogenic nature.

Conclusion
In conclusion, healthcare settings prioritize proper sterilization to prevent infections and ensure patient safety. Adherence to standardized procedures and guidelines from regulatory bodies like the CDC and WHO is crucial. Inadequate sterilization leads to serious consequences, including surgical site infections and HAIs. Healthcare facilities must commit to robust sterilization protocols and quality assurance measures. Prioritizing proper sterilization upholds patient safety and quality care, ensuring optimal surgical outcomes.